SkCanvas
========
*The drawing context*
Preview
-------
Here is an example of a set of drawing commands to draw a filled
heptagram. This function can be cut and pasted into
[fiddle.skia.org](https://fiddle.skia.org/).
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
const SkScalar scale = 256.0f;
const SkScalar R = 0.45f * scale;
const SkScalar TAU = 6.2831853f;
SkPath path;
path.moveTo(R, 0.0f);
for (int i = 1; i < 7; ++i) {
SkScalar theta = 3 * i * TAU / 7;
path.lineTo(R * cos(theta), R * sin(theta));
}
path.close();
SkPaint p;
p.setAntiAlias(true);
canvas->clear(SK_ColorWHITE);
canvas->translate(0.5f * scale, 0.5f * scale);
canvas->drawPath(path, p);
}
 Details
-------
SkCanvas is the drawing context for Skia. It knows where to direct the
drawing (i.e. where the screen of offscreen pixels are), and maintains
a stack of matrices and clips. Note however, that unlike similar
contexts in other APIs like postscript, cairo, or awt, Skia does not
store any other drawing attributes in the context (e.g. color, pen
size). Rather, these are specified explicitly in each draw call, via a
SkPaint.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->save();
canvas->translate(SkIntToScalar(128), SkIntToScalar(128));
canvas->rotate(SkIntToScalar(45));
SkRect rect = SkRect::MakeXYWH(-90.5f, -90.5f, 181.0f, 181.0f);
SkPaint paint;
paint.setColor(SK_ColorBLUE);
canvas->drawRect(rect, paint);
canvas->restore();
}
Details
-------
SkCanvas is the drawing context for Skia. It knows where to direct the
drawing (i.e. where the screen of offscreen pixels are), and maintains
a stack of matrices and clips. Note however, that unlike similar
contexts in other APIs like postscript, cairo, or awt, Skia does not
store any other drawing attributes in the context (e.g. color, pen
size). Rather, these are specified explicitly in each draw call, via a
SkPaint.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->save();
canvas->translate(SkIntToScalar(128), SkIntToScalar(128));
canvas->rotate(SkIntToScalar(45));
SkRect rect = SkRect::MakeXYWH(-90.5f, -90.5f, 181.0f, 181.0f);
SkPaint paint;
paint.setColor(SK_ColorBLUE);
canvas->drawRect(rect, paint);
canvas->restore();
}
 The code above will draw a rectangle rotated by 45 degrees. Exactly
what color and style the rect will be drawn in is described by the
paint, not the canvas.
Check out more detailed info on [creating a SkCanvas object](canvas).
To begin with, we might want to erase the entire canvas. We can do
this by drawing an enormous rectangle, but there are easier ways to do
it.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
SkPaint paint;
paint.setColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
canvas->drawPaint(paint);
}
This fills the entire canvas (though respecting the current clip of
course) with whatever color or shader (and xfermode) is specified by
the paint. If there is a shader in the paint, then it will respect the
current matrix on the canvas as well (see SkShader). If you just want
to draw a color (with an optional xfermode), you can just call
drawColor(), and save yourself having to allocate a paint.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->drawColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
}
All of the other draw APIs are similar, each one ending with a paint
parameter.
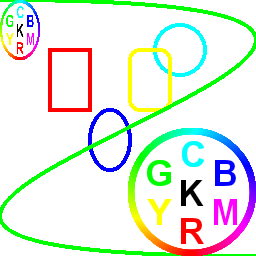
SkBitmap source;
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->drawColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
SkPaint paint;
paint.setStyle(SkPaint::kStroke_Style);
paint.setStrokeWidth(4);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorRED);
SkRect rect = SkRect::MakeXYWH(50, 50, 40, 60);
canvas->drawRect(rect, paint);
SkRRect oval;
oval.setOval(rect);
oval.offset(40, 60);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorBLUE);
canvas->drawRRect(oval, paint);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorCYAN);
canvas->drawCircle(180, 50, 25, paint);
rect.offset(80, 0);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorYELLOW);
canvas->drawRoundRect(rect, 10, 10, paint);
SkPath path;
path.cubicTo(768, 0, -512, 256, 256, 256);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorGREEN);
canvas->drawPath(path, paint);
canvas->drawImage(image, 128, 128, &paint);
SkRect rect2 = SkRect::MakeXYWH(0, 0, 40, 60);
canvas->drawImageRect(image, rect2, &paint);
SkPaint paint2;
const char text[] = "Hello, Skia!";
canvas->drawText(text, strlen(text), 50, 25, paint2);
}
The code above will draw a rectangle rotated by 45 degrees. Exactly
what color and style the rect will be drawn in is described by the
paint, not the canvas.
Check out more detailed info on [creating a SkCanvas object](canvas).
To begin with, we might want to erase the entire canvas. We can do
this by drawing an enormous rectangle, but there are easier ways to do
it.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
SkPaint paint;
paint.setColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
canvas->drawPaint(paint);
}
This fills the entire canvas (though respecting the current clip of
course) with whatever color or shader (and xfermode) is specified by
the paint. If there is a shader in the paint, then it will respect the
current matrix on the canvas as well (see SkShader). If you just want
to draw a color (with an optional xfermode), you can just call
drawColor(), and save yourself having to allocate a paint.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->drawColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
}
All of the other draw APIs are similar, each one ending with a paint
parameter.
SkBitmap source;
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->drawColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
SkPaint paint;
paint.setStyle(SkPaint::kStroke_Style);
paint.setStrokeWidth(4);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorRED);
SkRect rect = SkRect::MakeXYWH(50, 50, 40, 60);
canvas->drawRect(rect, paint);
SkRRect oval;
oval.setOval(rect);
oval.offset(40, 60);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorBLUE);
canvas->drawRRect(oval, paint);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorCYAN);
canvas->drawCircle(180, 50, 25, paint);
rect.offset(80, 0);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorYELLOW);
canvas->drawRoundRect(rect, 10, 10, paint);
SkPath path;
path.cubicTo(768, 0, -512, 256, 256, 256);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorGREEN);
canvas->drawPath(path, paint);
canvas->drawImage(image, 128, 128, &paint);
SkRect rect2 = SkRect::MakeXYWH(0, 0, 40, 60);
canvas->drawImageRect(image, rect2, &paint);
SkPaint paint2;
const char text[] = "Hello, Skia!";
canvas->drawText(text, strlen(text), 50, 25, paint2);
}
 In some of the calls, we pass a pointer, rather than a reference, to
the paint. In those instances, the paint parameter may be null. In all
other cases the paint parameter is required.
Next: [SkPaint](/user/api/skpaint)
In some of the calls, we pass a pointer, rather than a reference, to
the paint. In those instances, the paint parameter may be null. In all
other cases the paint parameter is required.
Next: [SkPaint](/user/api/skpaint)
 Details
-------
SkCanvas is the drawing context for Skia. It knows where to direct the
drawing (i.e. where the screen of offscreen pixels are), and maintains
a stack of matrices and clips. Note however, that unlike similar
contexts in other APIs like postscript, cairo, or awt, Skia does not
store any other drawing attributes in the context (e.g. color, pen
size). Rather, these are specified explicitly in each draw call, via a
SkPaint.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->save();
canvas->translate(SkIntToScalar(128), SkIntToScalar(128));
canvas->rotate(SkIntToScalar(45));
SkRect rect = SkRect::MakeXYWH(-90.5f, -90.5f, 181.0f, 181.0f);
SkPaint paint;
paint.setColor(SK_ColorBLUE);
canvas->drawRect(rect, paint);
canvas->restore();
}
Details
-------
SkCanvas is the drawing context for Skia. It knows where to direct the
drawing (i.e. where the screen of offscreen pixels are), and maintains
a stack of matrices and clips. Note however, that unlike similar
contexts in other APIs like postscript, cairo, or awt, Skia does not
store any other drawing attributes in the context (e.g. color, pen
size). Rather, these are specified explicitly in each draw call, via a
SkPaint.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->save();
canvas->translate(SkIntToScalar(128), SkIntToScalar(128));
canvas->rotate(SkIntToScalar(45));
SkRect rect = SkRect::MakeXYWH(-90.5f, -90.5f, 181.0f, 181.0f);
SkPaint paint;
paint.setColor(SK_ColorBLUE);
canvas->drawRect(rect, paint);
canvas->restore();
}
 The code above will draw a rectangle rotated by 45 degrees. Exactly
what color and style the rect will be drawn in is described by the
paint, not the canvas.
Check out more detailed info on [creating a SkCanvas object](canvas).
To begin with, we might want to erase the entire canvas. We can do
this by drawing an enormous rectangle, but there are easier ways to do
it.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
SkPaint paint;
paint.setColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
canvas->drawPaint(paint);
}
This fills the entire canvas (though respecting the current clip of
course) with whatever color or shader (and xfermode) is specified by
the paint. If there is a shader in the paint, then it will respect the
current matrix on the canvas as well (see SkShader). If you just want
to draw a color (with an optional xfermode), you can just call
drawColor(), and save yourself having to allocate a paint.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->drawColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
}
All of the other draw APIs are similar, each one ending with a paint
parameter.
SkBitmap source;
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->drawColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
SkPaint paint;
paint.setStyle(SkPaint::kStroke_Style);
paint.setStrokeWidth(4);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorRED);
SkRect rect = SkRect::MakeXYWH(50, 50, 40, 60);
canvas->drawRect(rect, paint);
SkRRect oval;
oval.setOval(rect);
oval.offset(40, 60);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorBLUE);
canvas->drawRRect(oval, paint);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorCYAN);
canvas->drawCircle(180, 50, 25, paint);
rect.offset(80, 0);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorYELLOW);
canvas->drawRoundRect(rect, 10, 10, paint);
SkPath path;
path.cubicTo(768, 0, -512, 256, 256, 256);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorGREEN);
canvas->drawPath(path, paint);
canvas->drawImage(image, 128, 128, &paint);
SkRect rect2 = SkRect::MakeXYWH(0, 0, 40, 60);
canvas->drawImageRect(image, rect2, &paint);
SkPaint paint2;
const char text[] = "Hello, Skia!";
canvas->drawText(text, strlen(text), 50, 25, paint2);
}
The code above will draw a rectangle rotated by 45 degrees. Exactly
what color and style the rect will be drawn in is described by the
paint, not the canvas.
Check out more detailed info on [creating a SkCanvas object](canvas).
To begin with, we might want to erase the entire canvas. We can do
this by drawing an enormous rectangle, but there are easier ways to do
it.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
SkPaint paint;
paint.setColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
canvas->drawPaint(paint);
}
This fills the entire canvas (though respecting the current clip of
course) with whatever color or shader (and xfermode) is specified by
the paint. If there is a shader in the paint, then it will respect the
current matrix on the canvas as well (see SkShader). If you just want
to draw a color (with an optional xfermode), you can just call
drawColor(), and save yourself having to allocate a paint.
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->drawColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
}
All of the other draw APIs are similar, each one ending with a paint
parameter.
SkBitmap source;
void draw(SkCanvas* canvas) {
canvas->drawColor(SK_ColorWHITE);
SkPaint paint;
paint.setStyle(SkPaint::kStroke_Style);
paint.setStrokeWidth(4);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorRED);
SkRect rect = SkRect::MakeXYWH(50, 50, 40, 60);
canvas->drawRect(rect, paint);
SkRRect oval;
oval.setOval(rect);
oval.offset(40, 60);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorBLUE);
canvas->drawRRect(oval, paint);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorCYAN);
canvas->drawCircle(180, 50, 25, paint);
rect.offset(80, 0);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorYELLOW);
canvas->drawRoundRect(rect, 10, 10, paint);
SkPath path;
path.cubicTo(768, 0, -512, 256, 256, 256);
paint.setColor(SK_ColorGREEN);
canvas->drawPath(path, paint);
canvas->drawImage(image, 128, 128, &paint);
SkRect rect2 = SkRect::MakeXYWH(0, 0, 40, 60);
canvas->drawImageRect(image, rect2, &paint);
SkPaint paint2;
const char text[] = "Hello, Skia!";
canvas->drawText(text, strlen(text), 50, 25, paint2);
}
 In some of the calls, we pass a pointer, rather than a reference, to
the paint. In those instances, the paint parameter may be null. In all
other cases the paint parameter is required.
Next: [SkPaint](/user/api/skpaint)
In some of the calls, we pass a pointer, rather than a reference, to
the paint. In those instances, the paint parameter may be null. In all
other cases the paint parameter is required.
Next: [SkPaint](/user/api/skpaint)