[+] IProtocolStack::AppendSingleFrameProcessorEx [+] ICompressionInterceptor::FlushNextFrame [+] ICompressionInterceptor::ConfigureAutoFlushPerFrame |
||
|---|---|---|
| Include | ||
| Media | ||
| Source | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| Aurora.json | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
PREALPHA (in-dev, missing polish and APIs are volatile)
Minimum viable product ETA: September 2022
AuroraRuntime
The Aurora Runtime is a low level platform abstraction layer for modern cross-platform C++ development targeting powerful embedded and PC systems. Simply fetch a binary package for your toolchain or integrate the self-contained buildscripts into your applications build pipeline to get started.
Features
- Reduced C++ standard template library dependence (^1)
- High performance threading and synchronization primitives (os userland sched optimized)
- Async even driven subsystem with high perf sync primitives
- Abstract kernel file/net transaction, IPC, timer, semaphore, et al abstraction in the form of LoopQueues (eg, MacOS RunLoops)
- Asynchronous and synchronous IO (network, character, file, buffered, process, and io watcher)
- Optional event driven async programming paradigm
- Consoles; graphical and standard, file archives
- Logging; UTF-8 logger, common sink backends
- Debug and Telementry; asserts, exception logging, fio, nio backends
- Crypto ECC/[25519, P-384, P-256], [AES, RSA, X509], [common digests]
- Basic cmdline parsing from any module
- Exit and fatal save condition callbacks
- IPC
- Network [WIP]
- Random; secure and fast
- Hardware Info; memory and cpu info (including features, topology, e-core, and cache info)
- Software Stack Info (kernel, version, brand, build string, etc)
- FIO settings registry
- Compression
- Locale and encoding
- C++ utility templates and macros
- Follows all strings are UTF-8 convention
^1 bring your own types auROXTL
Links
API:
API Docs:
Tests and Examples: Hello Aurora
Build Pipeline: Aurora Build (Lua/Premake)
Donate / Other Links: Reece.SX
Discord: Invite
Support
| Platform | Support |
|---|---|
| NT/Win32-like | ✅ |
| NT/UWP | 🕖 |
| NT/GameOS | ❌ |
| Linux | 🕖 |
| FreeBSD 9 | ❌ |
| FreeBSD 11 | ❌ |
| XNU/NS-like | ❌ |
Performance
Performance of each system should ideally be that of the best implementation on the platform, and no worse than the STL. Due to heavyweight requirements and spiral model defined objectives, a handful of portable C libraries have been brought into achieve compression, crypto, alloc, and str formatting objectives using known good industry standard libraries. Footprint is expected to be on the heavier side for optimal performance (incl toll for C++ tradeoffs) and flexibility.
Runtime as of 2022-02-01 without the wxWidgets toolkit, with all compression libraries on Windows LTSC 2019:
DLL Disk: 4.2MB
Size Of Image: 0x50B000 (5MB)
Real Commit Charge of a Console App: 9.7MB
...the task manager lie: 3,168K (3.1MB -> less than our DLL)
...HWInfo reports
[13:07:38] [Info] | RamInfo Private Allocation: 10215424/71987290112 (^1)
[13:07:38] [Info] | RamInfo Address Space: 11669504/71987290112
^1 ...on LTSC 2019. Modern Windows 10 and 11 will return the exact task manager value of 3,168K (3.1MB).
Defer to benchmarks
Utilities
Aurora Sugar: Main Header, (*.)Utils.hpp
Aurora Macro Sugar: Main Header
Aurora Overloadable Type Declerations: Main Header
Logging
Logging is implemented through 2 subsystems, console and logging. Console provides IO abstraction to the logger subsystem sinks. Sinks are user implementable interfaces that can be either synchronous or asynchronous. Loggers are defined as an internal object the takes logger messages and dumps them to the relevant subscriber.
Flushing occurs at a fixed rate on a low prio background thread without any configuration requirement. The resources spent on the background thread is shared with the telemetry and debug subsystems to reduce the overall thread count of the runtime. Flushes also occur during panic events and other relevant problematic points.
Asynchronous logger sinks may double buffer log lines between the asynchronous callback and OnFlush callback, where the latter call is guaranteed after one or more delegated dispatch. The Windows Event Log backend takes advantage of this to multi-line group messages by approx time and log level.
Additionally, in the console subsystem, consoles that provide an input stream can be used in conjunction with the parse subsystem to provide basic command-based deserialization, tokenization, and dispatch of UTF-8 translated strings regardless of the system locale. Command processing comes under the namespace of consoles, not logging.
Exceptions
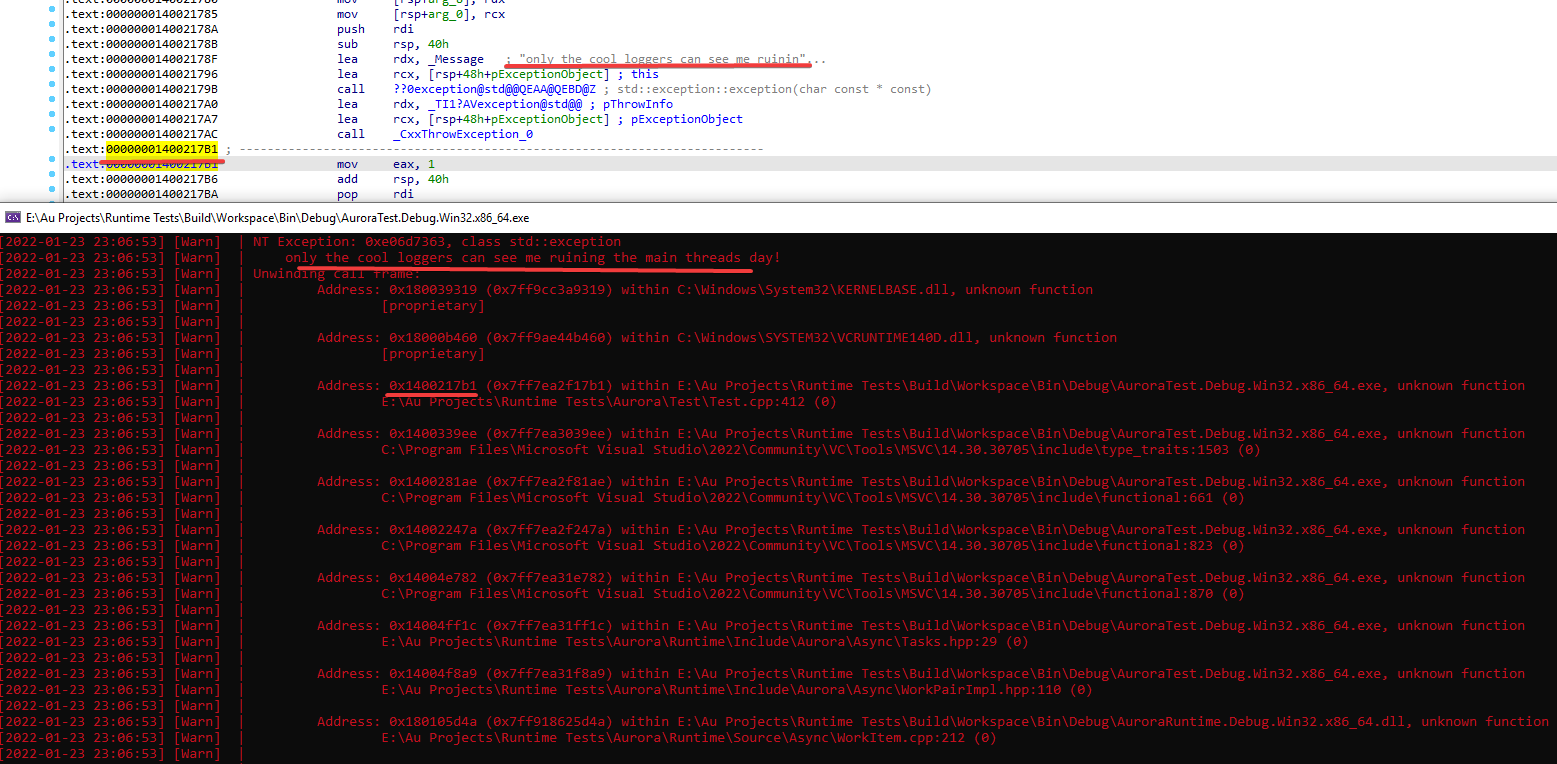
Through the use of compiler internal overloads, ELF hooking, and Win32
AddVectoredExceptionHandler, Aurora Runtime hooks exceptions at the time of throw, including
some out of ecosystem exceptions, providing detailed telemetry of the object type, object
string, and backtrace. In addition, the AuDebug namespace provides TLS based last-error and
last-backtrace methods.
EXCEPTIONS ARE NOT CONTROL FLOW...
- Aurora Runtime WILL attempt to mitigate exceptions in internal logic
- Aurora Runtime WILL NOT abuse exceptions to communicate failure
- Aurora Runtime WILL try to decouple internal exceptions from the API
- Aurora Runtime WILL NOT use anything that automatically crashes on exception catch (no-noexcept)
- Aurora Runtime WILL provide extended exception information to telemetry backends and through
the
AuDebugnamespace - Aurora Runtime WILL NOT make any guarantees of being globally-noexcept; however, it should be a safe assumption in non-critical environments
SysPanic can be used to format a std::terminate-like exit condition, complete with telemetry
data and safe cleanup.
Thread Primitives
The Aurora Runtime provides platform optimized threading primitives inheriting from a featureful IWaitable interface. Each method is guaranteed. Each primitive is user-land scheduler optimized.
struct IWaitable
{
virtual bool TryLock() = 0;
virtual void Lock(relativeTimeoutInMilliseconds) = 0;
virtual void Lock() = 0;
virtual void Unlock() = 0;
}
Included high performance primitives
- arbitrary condition variable ^1
- condition mutex
- condition variable
- critical section ^2
- event
- mutex
- semaphore
- rwlock ^3
- spinlocks
^1 Accepts any IWaitable as the mutex
^2 Reentrant Mutex
^3 Includes extended read to write upgrades and permits write-entrant read-routines to prevent
writer deadlocks.
Fixing problems in other scheduler apis
Problem one (1):
Most STL implementations have generally awful to unnecessarily inefficient abstraction.
Defer to libc++'s abuse of spin while (cond) yield loops and msvc/stl's painfully slow
std::mutex and semaphore primitives.
Problem Two (2):
Moving to or from linux, macos, bsd, and win32 under varous kernels, there is no one
standard (even in posix land) for the key thread primitives.
Bonus point NT (3):
The userland CriticalSection/CV set of APIs suck, lacking timeouts and try lock
Bonus point UNIX (4):
No wait multiple mechanism
1, 2, 3: Use the high performance AuThreadPrimitives objects
4: Consider using loop sources, perhaps with the async subsystem, in your async application. Performance of loop sources will vary wildly between platforms, always being generally worse than the high performance primitives. They should be used to observe kernel-level signalable resources.
4 ex: Windows developers could use loop sources as a replacement to WaitMultipleObjects with more overhead
IO
The Aurora Runtime implements a multiple io wait loop sub-subsystem, file io, network io, various adapters and connectors, io processors, io/character, io/buffered, and other such concepts to aid with writing low-level cross-platform IO.
An important note about texting encoding. Stdin, file encoding, text decoders, and other IO resources work with codepage UTF-8 as the internal encoding scheme. String overloads and dedicated string APIs in the IO subsystem will always write BOM prefixed UTF-8, and attempt to read a BOM to translate any other arbitrary user generated text input to UTF-8.
Loop
The Aurora Runtime implements a kernel-scheduler optimized IO subsystem for managing GUIs, Network AIO, File AIO, IPC AIO, and thread synchronization objects through loop the loop subsystem.
ILoopSource is an interface defined by the loop subsystem for IO objects with a signalable state. Attached to an ILoopQueue, the ILoopQueue will provide wait-on and similar functionality; and subscription notifications of signal state change. ILoopQueue's are thread-safe allowing for cross-thread or mid-wait work scheduling. Subscription notifications allow for optimized loop source removal or no-action/non-removal replies from subscription implementer. In addition to the synchronization provided by the ILoopQueue, the ILoopSource interface permits arbitrary is-signaled-and-latch (TryLock) queries and timed-wait (WaitOn) calls on a per IO object basis.
IPC
Included in the IPC subsystem are pipes, as used by AuProcesses; events; mutexes; semaphores; and shared memory views. IPC objects are exported by an internally generated non-standard string which contains platform specific information to import such object in a compatible application. Aurora IPC is not bound by processes bound by a common worker, instead, UNIX sockets and procfs are used to implement IPC within the applications namespace/sandbox.
FIO
A simple file stream interface is provided by an Open function which accepts an Aurora path and
an advisory lock level. However, all such functions are blocking in face of platform specific
asynchronous alternatives. An alternative IAsyncFileStream is provided to supply the user with
an supplier of IAsyncTransaction's - an overlapped IO style interface for starting a read/write
transaction, registering an APC-like callback, requesting a loop subsystem waitable object, and
clearing the request. AIO is backed by io_submit under Linux, POSIX AIO under BSD, and Overlapped
IO under NT. A glibc approach of spamming threads akin to libuv and skipping the synchronization
on completion step isn't our style. Instead, you are reliant on the native async capabilities of the
underlying operating system. Special consideration must be made for alignment, cached/uncached access,
and supported file systems.
Additional utility functions exist outside of the two file interfaces for: stat, directory iteration, UTF-8 string reading and writing, blocking binary read/writes, and more.
Paths
We assume all paths are messy. Incorrect splitters, double splitters, relative paths, and keywords are resolved internally.
No URL or path builder, data structure to hold a tokenized URI expression, or similar concept exists in the codebase.
All string paths are simply expanded, similar to MSCRT's fullpath or UNIX's realpath, at time of usage.
| Expression | Meaning |
|---|---|
Path[0] == '.' |
Current Working Directory |
Path[0] == '^' |
Executable module's Directory |
Path[0] == '~' |
User Profile Storage + SDK brand |
Path[0] == '!' |
All User Shared Storage + SDK brand |
.. |
Go up a directory |
/ |
Agnostic Directory Splitter |
\ |
Agnostic Directory Splitter |
. [SPLITTER] |
Nothing |
Resources
The Aurora Runtime provides reports system, application, and user specific paths under the Aurora::IO::FS subsystem.
These include the users home directory, a per vendor sandboxed application user directory, a per vendor sandboxed application
all users directory, the user-installable program directory, the user's real home directory, and other such relevant paths.
Networking
Character IO
Proccesses
The Aurora Runtime provides child process monitoring, asynchronous child stdin/out/err transactions, child synchronization (via a primitive threading event and an io event), process spawning, file opening, and url opening functionality.
Locale
Encoding and decoding of UTF-8, UTF-16, UTF-32, GBK, GB-2312, and SJIS is supported through platform provided decoders. System localization information, including system codepage, country, and system language, is provided by the envrionment variables which are available, OS specific interfaces, or the user overload mechanism.
Memory
Allocator
Objects are allocated across API/Module boundaries. So long as the high level API design isn't horribly inefficient to an extent that cache invalidation and indirect lookups are minimalized, object-heavy code can optimized. On modern hardware, legitmate indirect branching versus short jumps aren't so expensive between modules in real world usage; and in combination with a fast enough allocator, there is little reason why couldn't achieve reasonable OOP performance through a C-with-classes-like API.
As for allocation, we generally expect a dependence on Microsoft's mimalloc. Linking against the Aurora Runtime in the Aurora
Ecosystem will automatically replace global allocators with Aurora::Memory, which in turn, proxies any other suitable allocator
interface with extended zero, array, and alignment respecting APIs. A suitably fast allocator, such as mimalloc, should reduce the
cost of the OOP design.
Memory Heap
Aurora provides a heap allocator for dividing up a large preallocated region of memory
Shared Pointers
Memory objects, including shared pointers, and the object allocation model is defined by AuROXTL. The AuSPtr class template
is backed by the standard std::shared_ptr, extended by #include <auROXTL/auMemoryModel.hpp>, in the default configuration.
AuROXTL memory primitives, and most STL containers, are source compatible with the base STL classes, such that any Aurora specific behaviour is lost during type reduction.
There are benefits of using the Aurora extended classes, include redefining null dereference on shared ptrs to throw an AU_THROW_STRING. Without support for native behaviour within the C++ driver, such features are rather expensive using the performace hacks we have available (outside of ripping the compiler apart to emit special debug info for hacky trap handlers). Arguably, it's an experiment worth trying now that modern hardware can make up for software and microcode flaws; and architecture translation. Most users probably wont even notice the performance loss, until it saves them from a hard crash and they realize dereferences are bloated. This is default behaviour, and can be easily disabled or configured from within your ecosystem's AuroraConfiguration.h to globally modify the behaviour and subsequent ABI of the AuSPtr's.
Types:
AuSPtr<Type_t>
AuWPtr<Type_t>
AuUPtr<Type_t, Deleter_t>
Functions:
AuSPtr<T> AuMakeShared<T>(Args&& ...)
AuSPtr<T> AuUnsafeRaiiToShared<T>(T *)
AuSPtr<T> AuUnsafeRaiiToShared<T>(AuUPtr<T>)
Macros:
_new (pseudo no-throw new operator)
AuSPtr<This_T> AuSharedFromThis()
AuWPtr<This_T> AuWeakFromThis()
AuFunction<...> AuBindThis(This_t *::?, ...)
Note
Aurora provides a bring your own container and shared pointer model overloadable in your configuration header.
User-overloadable type declerations and generic access utilities are defined under auROXTL
Debug
Error Markers
SysPushError[EFailureCategory shorthand] can be used to include additional side-channel telemetry information about the execution of a program. SysPushError_(...) takes a string format sequence and a variadic sequence of substitute values - or no arguments whatsoever.
Example:
IBufferedCharacterConsumer *BufferConsumerFromProviderNew(const AuSPtr<ICharacterProvider> &provider)
{
if (!provider)
{
SysPushErrorArg("Missing ICharacterProvider");
return {};
}
return _new BufferedCharacterConsumer(provider);
}
Asserts
[TODO]
Example:
Debug, Release, and Ship (all) assertions:
SysAssert(AuFunction{}, "unexpected default function")
Debug and Release (debug and optimized ship-with-debug) assertions:
SysAssertDbg(AuFunction{}, "unexpected default function")
Something went wrong
You should ensure AuDebug::CheckErrors() or a SysPushError-like function is called to ensure enchanced TLS-state telemetry is captured. AuDebug::PrintErrors() will print the the errors gathered by the debug subsystem for telemetry purposes. These may include the crts errno, the last reported posix return value, the last Win32 error code, and/or last reported microkernel error.
Example
Try/Catch:
try
{
}
catch (...)
{
SysPushErrorCatch(); // THIS IS NOT REQUIRED FOR EXCEPTION TELEMETRY
}
Windows System Error Messages:
CRT:
POSIX:
Binding
Aurora Runtime provides C++ APIs; however, it should be noted that two libraries are used to extend interfaces and enums
to help with porting and internal utility access. One, AuroraEnums, wraps basic enumerations and provides value vectors;
value strings; look up; iteration; and more. The other, AuroraInterfaces, provides TWO class types for each virtual interface.
Each interface can be backed by a; C++ class method overriding a superclass's virtual ...(...) = 0; method, or a AuFunctional
-based structure.
It should be noted that most language bindings and generator libraries (^swig, v8pp, nbind, luabind) work with shared pointers.
Other user code may wish to stuff pointers into a machineword-sized space, whether its a C library, a FFI, or a size constraint.
One handle or abstraction layer will be required to integrate the C++ API into the destination platform, and assuming we have a
C++ language frontend parsing our API, we can use AuSPtr for all caller-to-method constant reference scanerios.
Furthermore, AuSPtrs can be created, without a deletor, using AuUnsafeRaiiToShared(unique/raw pointer). To solve the raw
pointer issue, AuSPtrs are created in the public headers with the help of exported/default visibility interface create and
destroy functions. These APIs provide raw pointers to public C++ interfaces, and as such, can be binded using virtually any
shim generator. Method and API mapping will likely involve manual work from the library developer to reimplement AU concepts
under their language runtime instead of using the C++ platform, or at least require manual effort to shim or map each runtime
prototype into something more sane across the language barrier.
Memory is generally viewed through a std::span like concept called MemoryViews. MemoryViewRead and MemoryViewWrite
provide windows into a defined address range. MemoryViewStreamRead and MemoryViewStreamWrite expand upon this concept by
accepting an additional offset (AuUInt &: reference) that is used by internal APIs to indicate how many bytes were written
or read from a given input region. Such requirement came about from so many APIs, networking, compression, encoding, doing the
exact same thing in different not-so-portable ways. Unifying memory access to 4 class types should aid with SWIG prototyping.
Unrelated note, structure interfacing with questionable C++ ABI reimplementations is somewhat sketchy in FFI projects (^ CppSharp) can lead to some memory leaks.
Aurora Async
The Aurora Runtime offers an optional asynchronous task driven model under the AuAsync namespace. Featuring promises, thread group pooling, functional-to-task wrapping, and task-completion callback-task-dispatch idioms built around 3 concepts.
Example:
Strings
The auROXTL header only library defines an AuString type as an std::string; however, it should be assumed this type represents
a binary blob of UTF-8. Further locale processing is delegated to Aurora::Locale[::Encoding]
Dependencies
Aurora
- AuroraPipeline Include ^2
- auROXTL ^2
- AuroraEnum ^1
- AuroraInterfaces ^1
- AuroraForEach ^1
Crypto (third party)
- LibTomCrypt / LibTomMath ^5
- mbedTLS
Compression (third party)
Utility (third party)
^1 Include-only macro library
^2 Provides core utilities and stl decoupling
^3 Provides platform information, included by default by the Aurora build pipeline
^4 C++ 20 saw another pathetic adoption attempt of an open source library, this one actually passed, but hardly
anyone implements std::format. Not to mention such is only a subset of the original library.
^5 Public Domain
^6 Potentially STL heavy, still potentially portable w/ a modern-ish toolchain
Philosophies
-
Assume C++17 language support in the language driver
-
Use AuXXX type bindings for std types, allow customers to overload the std namespace
We assume some containers and utility APIs exist, but where they come from is up to you -
Keep the code and build chain simple such that any C++ developer could maintain their own software stack built around aurora components.
-
Dependencies and concepts should be cross-platform, cross-architecture, cross-ring friendly
It is recommended to fork and replace any legacy OS specific code with equivalent AuroraRuntime concepts, introducing a circular dependency with the Aurora Runtime
APIs shouldn't be designed around userland, mobile computing, or desktop computing; AuroraRuntime must provide a common backbone for all applications.
Locale and user-info APIs will be limited due to the assumption userland is not a concept
-
Dependencies, excluding core reference algorithms (eg compression), must be rewritten and phased out over time.
-
Dependencies should not be added if most platforms provide some degree of native support
Examples:
-> Don't depend on a pthread shim for windows; implement the best thread
primitives that lie on the best possible api for them
-> Don't depend on ICU when POSIX's iconv and Win32's multibyte apis cover
everything a conservative developer cares about; chinese, utf-16, utf-8,
utf-32 conversion, on top of all the ancient windows codepages -
Dependencies should only be added conservatively when it saves development time and provides production hardening
Examples:
-> Use embedded crypto libraries; libtomcrypt, libtommath
->> While there are some bugs in libtomcrypt and others, none appear to
cryptographically cripple the library. Could you do better?
-> Use portable libraries like mbedtls, O(1) heap, mimalloc
->> Writing a [D]TLS/allocator stack would take too much time
->> Linking against external allocators, small cross-platform utilities, and
so on is probably fine
-> Shim libcurl instead of inventing yet another http stack