No-Try: true Change-Id: I1b9b1be36c9ed2d574de681b90b98e56f45e70fa Reviewed-on: https://skia-review.googlesource.com/c/174588 Auto-Submit: Hal Canary <halcanary@google.com> Reviewed-by: Hal Canary <halcanary@google.com> Commit-Queue: Hal Canary <halcanary@google.com>
4.3 KiB
4.3 KiB
Skia's Stable C API
EXPERIMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL
DO NOT USE — FOR INTERNAL TESTING ONLY
DO NOT USE — FOR INTERNAL TESTING ONLY
Several issues hinder the development of a stable ABI (application binary interface) for Skia:
- Skia's C++ API changes a lot from version to version. Skia's two largest clients, Android and Chrome, are kept up to date by the Skia team, but that can not happen for every client.
- Skia's headers will only match the compiled skia libraries if configured identically.
To mitigate these two issues, Skia is experimenting with the introduction of a C API. This will change more slowly than the C++ interface and, once API version 1.0.0 is announced, backwards-incompatable changes will be avoided whenever possible.
Here is an example program that uses the C api. To try it out, get the file
skia-c-example.c.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sk_data.h"
#include "sk_image.h"
#include "sk_canvas.h"
#include "sk_surface.h"
#include "sk_paint.h"
#include "sk_path.h"
static sk_surface_t* make_surface(int32_t w, int32_t h) {
sk_imageinfo_t info;
info.width = w;
info.height = h;
info.colorType = sk_colortype_get_default_8888();
info.alphaType = PREMUL_SK_ALPHATYPE;
return sk_surface_new_raster(&info, NULL);
}
static void emit_png(const char* path, sk_surface_t* surface) {
sk_image_t* image = sk_surface_new_image_snapshot(surface);
sk_data_t* data = sk_image_encode(image);
sk_image_unref(image);
FILE* f = fopen(path, "wb");
fwrite(sk_data_get_data(data), sk_data_get_size(data), 1, f);
fclose(f);
sk_data_unref(data);
}
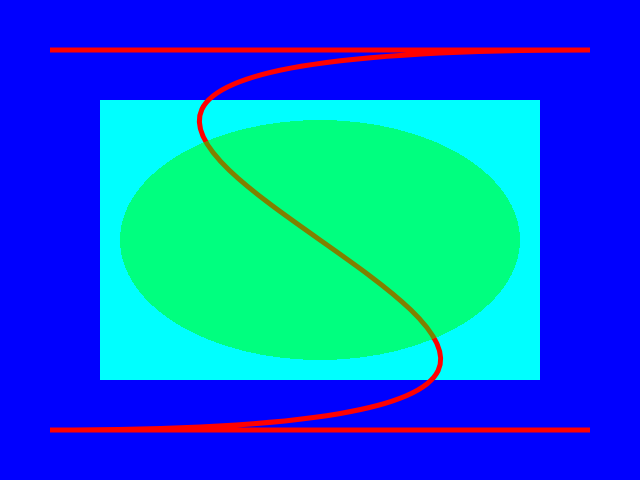
void draw(sk_canvas_t* canvas) {
sk_paint_t* fill = sk_paint_new();
sk_paint_set_color(fill, sk_color_set_argb(0xFF, 0x00, 0x00, 0xFF));
sk_canvas_draw_paint(canvas, fill);
sk_paint_set_color(fill, sk_color_set_argb(0xFF, 0x00, 0xFF, 0xFF));
sk_rect_t rect;
rect.left = 100.0f;
rect.top = 100.0f;
rect.right = 540.0f;
rect.bottom = 380.0f;
sk_canvas_draw_rect(canvas, &rect, fill);
sk_paint_t* stroke = sk_paint_new();
sk_paint_set_color(stroke, sk_color_set_argb(0xFF, 0xFF, 0x00, 0x00));
sk_paint_set_antialias(stroke, true);
sk_paint_set_stroke(stroke, true);
sk_paint_set_stroke_width(stroke, 5.0f);
sk_path_t* path = sk_path_new();
sk_path_move_to(path, 50.0f, 50.0f);
sk_path_line_to(path, 590.0f, 50.0f);
sk_path_cubic_to(path, -490.0f, 50.0f, 1130.0f, 430.0f, 50.0f, 430.0f);
sk_path_line_to(path, 590.0f, 430.0f);
sk_canvas_draw_path(canvas, path, stroke);
sk_paint_set_color(fill, sk_color_set_argb(0x80, 0x00, 0xFF, 0x00));
sk_rect_t rect2;
rect2.left = 120.0f;
rect2.top = 120.0f;
rect2.right = 520.0f;
rect2.bottom = 360.0f;
sk_canvas_draw_oval(canvas, &rect2, fill);
sk_path_delete(path);
sk_paint_delete(stroke);
sk_paint_delete(fill);
}
int main() {
sk_surface_t* surface = make_surface(640, 480);
sk_canvas_t* canvas = sk_surface_get_canvas(surface);
draw(canvas);
emit_png("skia-c-example.png", surface);
sk_surface_unref(surface);
return 0;
}
Example
The following proof-of-concept workflow currently works on MacOS and Ubuntu.
-
Compile Skia as a shared library:
cd ...../skia bin/sync gn gen out/Shared --args='is_official_build=true is_component_build=true' ninja -C out/Shared SKIA_LIB_DIR="${PWD}/out/Shared" -
Compile, link, and run the example program:
cc -o skia-c-example -I include/c \ experimental/c-api-example/skia-c-example.c \ "$SKIA_LIB_DIR"/libskia.* -Wl,-rpath -Wl,"$SKIA_LIB_DIR" ./skia-c-example bin/sysopen skia-c-example.png